Article Number: CPU-100
To improve the reliability and performance of AMD processors, it is critical that certain precautions are taken when using and handling them. This document describes the best practices and the precautions required to reduce the risk of damages to the processor, and is divided into following sections:
Electrical Power Damage
External Power Sources which do not conform to the specifications of the processor can cause irreversible damage to the processor. Processor damage is usually not visible to the user because the damage is inside the processor.
Sources of this damage include
- Voltage spikes
- Power supply failures
- Motherboard voltage supply failures etc.
Avoiding External Electrical Power Damage
 Ensure Proper Part Insertion
Ensure Proper Part Insertion
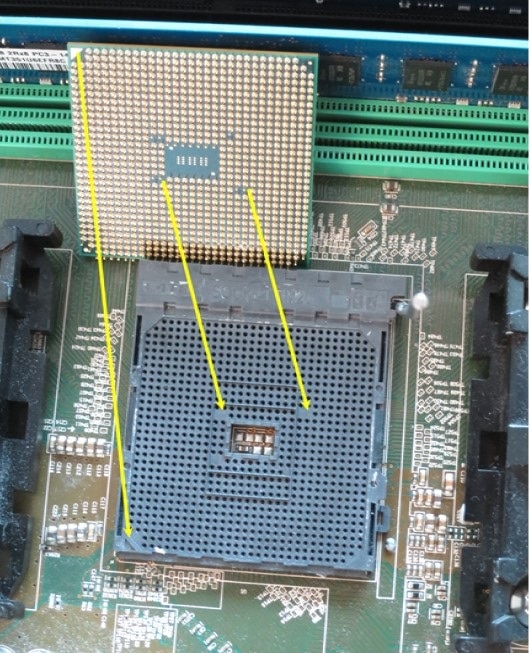
AMD processors require a proper insertion orientation into the socket to ensure all pins connect correctly to the motherboard. The motherboard socket should have missing holes in the pin array that mirror the missing pin pattern on the bottom of the socket. Care must be taken to orient the processor pin pattern so that the pins will match the socket pin pattern prior to insertion.
If properly oriented, the processor should drop into the socket without applying any force on the processor to achieve insertion. If it does not drop into the socket, the processor may be misaligned or have bent pins. The processor should never be forced into the socket. Forcing the processor into the socket can bend the pins and damage the processor. Forcing the socket can also be an indication of incorrect orientation, which can cause damage when the power is applied.
Use Electrical Power Surge Protection
 The quality of your electrical power depend on your local utility infrastructure. Even for high quality systems, electrical storms can also bring about un-expected power surges/spike.
The quality of your electrical power depend on your local utility infrastructure. Even for high quality systems, electrical storms can also bring about un-expected power surges/spike.
Your PC computer should be connected to the electrical outlet with a high quality power surge protector.
This prevents power spikes from damaging any components in your PC. Any external connections to your PC should also be routed through this surge protector including any cable, LAN, USB or telephone lines. The surge protector should be connected to a good earth ground to ensure proper operation.

Avoiding damage during Installation and removal of system components
System components should never be installed inside a system case while the system is powered up. This includes the processor and any internally pluggable component such as internal graphics, audio, and network interface cards etc. Powered installation can not only damage the processor, it can also damage the component being installed.
Avoiding damage from hot plugging external system connectors
Connecting devices that do not comply with industry hot plugging specifications can be the source of electrical power damage, the source includes display connector, interface cards and/or USB port. It is good practice to always switch off the power of the monitor(s) and computer when connecting graphics cables.
For any USB components, AMD recommends only using USB components that have metal shielded connectors. An example of the metal shield is shown in the image. AMD also recommends disabling USB components with the operating system USB removal software function to avoid data corruption and also reduce the risk of damage.

Electrostatic Discharge
Electrostatic discharge can cause a range of harmful and permanent damage to electronic components including the processor. Static electricity is easily generated by humans as their clothes rub against each other or against the skin. The average person requires an Electrostatic Discharge of 3,000 volts before he or she feels it. An electronic component can be damaged with as little as 30 volts. A visible static spark is seen at 30,000 volts.
Some electronic components may not be damaged the first time a static discharge occurs. However, the effects of static discharge can be cumulative, weakening or eventually destroying a component. An Electrostatic Discharge event that damages a component is not recoverable. The component cannot be repaired. Electronic chips and memory modules are most susceptible to Electrostatic Discharge strikes.
Charges can build up over 100V very quickly and is not being noticed until a discharge happens. Therefore, Electrostatic Discharge precautions must be followed when handling any electronic device including processors (APU, GPU, CPU), computer components (memory, HDD etc.), motherboards and computer systems.
Best Practices
- Use a grounded Electrostatic Discharge mat, alternatively referred to as a grounding mat. An antistatic mat is a table mat that reduces the risk of electrostatic discharge while working with electrostatic sensitive equipment. The pictures blow show an example of an antistatic mat and the power socket required to correctly ground the mat.

- Avoid improper clothing – Do not wear any clothing that easily generates static such as a fleece or wool sweater.
- Disconnecting power cords - Disconnect all un-used hardware for the computer system (e.g. other power cords, monitor, and USB cables) except the computer power cord to power supply.
- Loose articles and accessories - To avoid accidental shorts and mechanical entanglement, remove jewelry and loose articles.
- Work from a standing position - Always stand when working inside the computer. If you are sitting on a chair or the floor, it can force more movements and generate more electrostatic charge especially for chairs with wheels.
- Work on grounded surfaces - Stand on a hard surface that is dissipative. The computer and other electrostatic sensitive devices should be on a table that is grounded.
- Make sure the power supply of your computer is connected to the surge protector (connected to your AC outlet).

- Before opening our computer, make sure the power supply is completely off but still is connected to the surge protector (connected to your AC outlet). If the power supply unit has a toggle switch, toggle the power supply unit to the off position.
- Wear proper fitting working wrist strap (fitted snuggly around your wrist not loosely; wrist strap should make good contact to your skin).
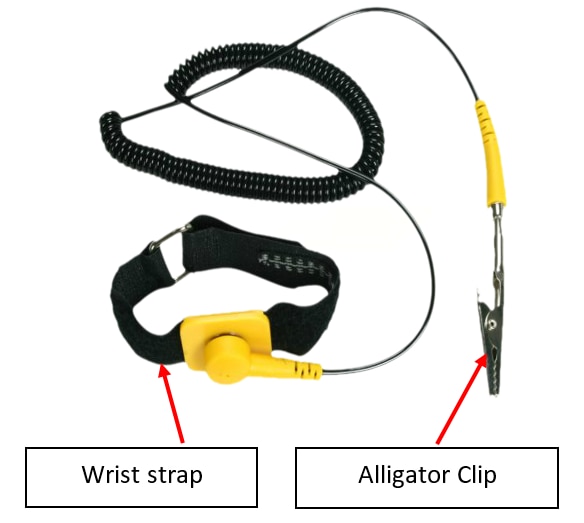

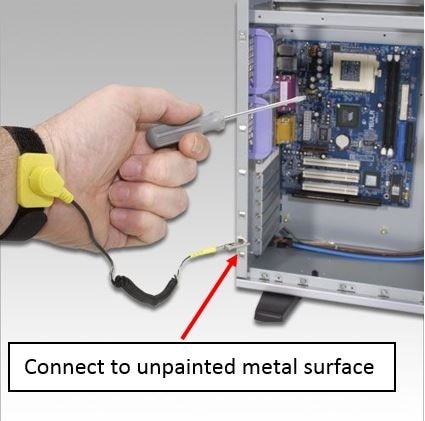
- Connect your wrist strap to an un-painted metal contact in your computer system. Make sure the connection is in place at all times. Simply connecting to case interior won't necessarily ground you -- the object must be connected to ground and must be capable of discharging electricity.

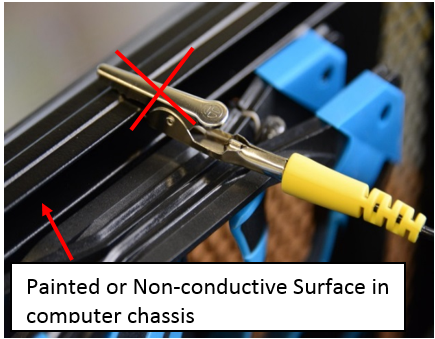
Do Not Connect to Painted or Non-Metallic Surfaces
Most modern gaming-grade cases have interior paint covering their metallic walls, so touching the paint will not ground you.
Store all computer hardware and component in Anti-static Electrostatic Discharge bags. Make sure the Electrostatic Discharge bag openings are closed and folded.
Thermal Overstress
Proper cooling of AMD processors is mandatory to avoid damaging the processor. Damage can occur very quickly if the processor is powered up without a heatsink present. AMD Processor-In-a-Box (PIB) includes a validated heatsink and fan.
If AMD processors are purchased without an AMD approved heatsink, the heatsink must be carefully chosen to ensure its rated heat dissipation capability meets or exceeds the power consumption of the processor. In addition, a good thermal interface material should be applied in a uniform layer over the surface of the processor lid to maximize the effectiveness of the heatsink. Good cooling ensures stable operation of the processor and prevents premature failure due to excessive operating temperatures.
Please see the following video for a proper installation of a new processor and heatsink/fan.
Prior to powering up the processor, the following checks should be made to ensure good cooling.
- Ensure an AMD approved heatsink/fan (HSF) is being used with the processor
- Ensure the HSF unit is properly installed on the processor
- Ensure the bottom of the HSF is leveled on the top of the processor
- Ensure a proper amount of thermal grease is installed between the HSF and processor
- If the heatsink is removed, ensure that there is still a good coating of grease and that the grease has not dried up since dry grease has poor heat transfer
- Ensure that the fan on the graphics card and processor’s heatsink is connected correctly and that it is spinning when the system is powered on
- Check whether there are any loose cables stopping the fan(s) from spinning or blocking the air flow within the system case
- Verify that the airflow within the system case is circulating correctly
- Air should flow in from the front of the case and out through the back of the case
- Make sure the HSF is locked down
Overclocking
Overclocking is the process of forcing a computer hardware component to operate faster than intended. It can boost the overall performance of the system, which can help improve benchmark scores and increase the number of frames per second (FPS) in 3D games. Unfortunately overclocking increases power consumption which leads to more heat generation and eventually processor damage. AMD does not support overclocking and cannot be held liable for any damage caused by the overclocking. Other side effects of overclocking include:
- System instability and/or lower performance
- Reduction of the lifespan of overclocked hardware
Disclaimer & Attribution
Disclaimer The information herein is for informational purposes only and may be of a preliminary or advance nature and is subject to change. Moreover, the information herein may contain technical inaccuracies, omissions and typographical errors. AMD makes no representations or warranties with respect to the accuracy or completeness of the contents of this report and AMD reserves the right to make revisions or changes to this report at any time without notice and without obligation to notify any person of such revisions or changes. No license, whether express, implied, arising by estoppels or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted by this publication.
AMD SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS ANY WARRANTIES RELATED TO THIS REPORT AND, EXCEPT AS MAY BE SET FORTH SEPARATELY IN YOUR PURCHASE AGREEMENT(S) WITH AMD, ANY WARRANTIES RELATED TO AMD’S PRODUCTS INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, OF FITNESS FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR OF NON-INFRINGEMENT OF ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT. IN NO EVENT WILL AMD BE LIABLE TO ANY PERSON FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL OR OTHER CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING FROM THE USE OF ANY INFORMATION CONTAINED HEREIN, EVEN IF AMD IS EXPRESSLY ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Attribution © 2016 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. AMD, the AMD Arrow logo and combinations thereof are trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. in the United States and/or other jurisdictions. Other names are for informational purposes only and may be trademarks of their respective owners.