

AI Technologies Bring Broad Industry Impact
AI is profoundly transforming workloads and industries, driving efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness. From automating processes in manufacturing and automotive to curbing financial fraud and accelerating medical research, businesses can harness the power of AI technologies to unlock new opportunities, optimize operations, and deliver value to customers in ways that were previously unimaginable.
AMD Powers The Full Range Of Data Center Workloads
Embracing AI in your enterprise can be overwhelming. Understanding how the AMD portfolio supports the full range of AI workloads can clarify your application requirements. Understanding how AI workloads are deployed and maintained in enterprise data centers helps clarifies infrastructure needs.


General Purpose
AI Inference
AI Training

Advancing Ideal AI Solutions
Free Up the Space and Energy to Accommodate AI in Your Data Center
Many data centers are already running at or near capacity in terms of available space or power or both.1 AMD EPYC processor-based servers offer leadership performance and efficiency to enable material workload consolidation, allowing more space and energy to support new AI workloads in your existing data centers.
Replace 100 old 2P Intel® Xeon® Platinum 8280 CPU-based servers with 14 new AMD EPYC™ 9965 CPU-based servers2
*to deliver a total of ~39,000 units of integer performance.

Up to 86% fewer servers

Up to 69% less power

Up to 65% lower 3-yr TCO
Help lower cost and TCO AMD EPYC™ 9965 CPU-based servers vs Intel® Xeon® Platinum 8592+ CPU-based servers2
*to deliver a total of ~39,000 units of integer performance.

Up to 60% fewer servers

Up to 40% less power

Up to 41% lower 3-yr TCO
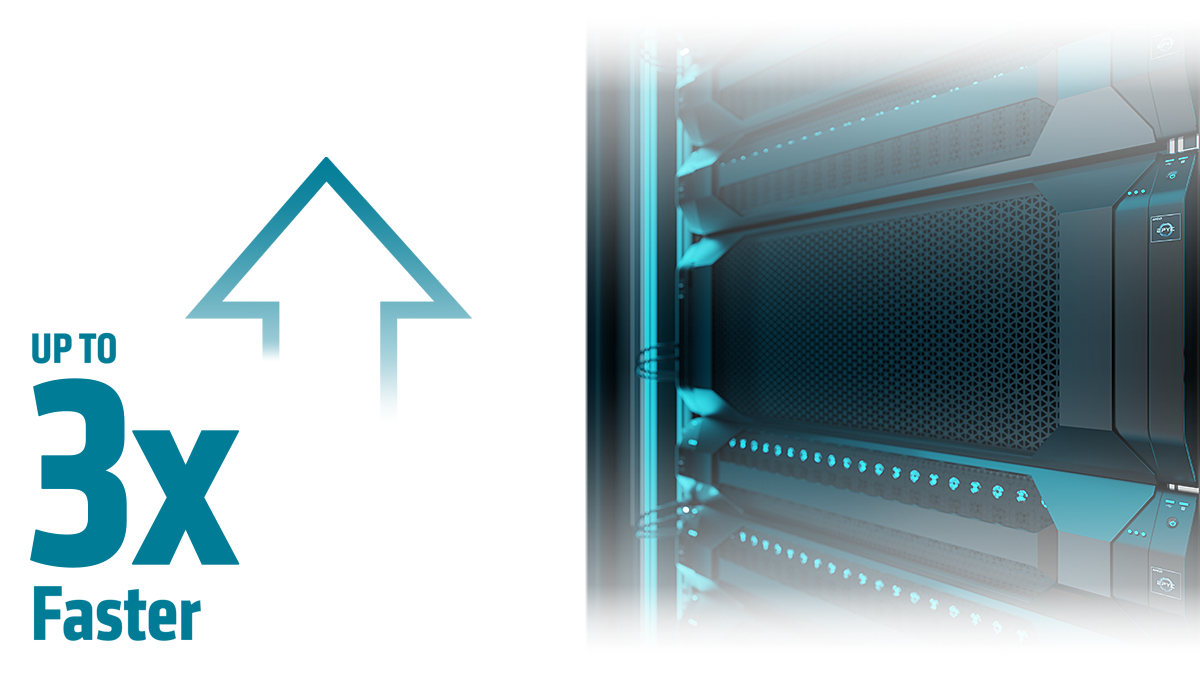

Leadership Inference Performance
AMD EPYC processor-based servers are the ideal CPU-based AI platform to run inference across a variety of models and use cases. AMD EPYC CPUs deliver the flexibility to support requirements ranging from real time inference to batch or offline inference.
192-core AMD EPYC™ 9965 processors deliver 3x the inference throughput of the top of stack 64-core Intel Xeon 8592+ processors (average runs/hour of 2P servers running the popular gradient boosting model XGBoost (Higgs Data Set) at FP32 precision).3

The Right Host CPU for GPUs
For running larger and more demanding AI workloads, GPUs are the right choice. Serving the GPUs to achieve maximum throughput is the job of the host CPU. To get the most out of these valuable GPUs, it is important to choose the right host platform. AMD EPYC processor-based servers feature the performance, scalability, compatibility, and energy efficiency to support hosting advanced GPU AI engines. Learn what CPU features are important for hosting GPUs.
Choose from hundreds of certified GPU-accelerated systems powered by AMD EPYC CPUs to speed AI workloads. View AMD Instinct™ GPU accelerated solutions .
Ask for other certified or validated GPU-accelerated solutions available from leading platform solution providers including Asus, Dell, Gigabyte, HPE, Lenovo, and Supermicro.


Customer Testimonials

Resources
Taking a Pragmatic Approach for AI-Ready Infrastructure
Investigate AI infrastructure strategies, focusing on rightsizing solutions in datacenter modernization, and optimizing CPU-GPU use for tasks of varying size and complexity.
Subscribe to Data Center Insights from AMD
Request Contact from an AMD EPYC Sales Expert
Footnotes
- Analysis based on AMD internal data
- 9xx5TCO-001B: This scenario contains many assumptions and estimates and, while based on AMD internal research and best approximations, should be considered an example for information purposes only, and not used as a basis for decision making over actual testing. The AMD Server & Greenhouse Gas Emissions TCO (total cost of ownership) Estimator Tool - version 1.12, compares the selected AMD EPYC™ and Intel® Xeon® CPU based server solutions required to deliver a TOTAL_PERFORMANCE of 39100 units of SPECrate2017_int_base performance as of October 10, 2024. This scenario compares a legacy 2P Intel Xeon 28 core Platinum_8280 based server with a score of 391 versus 2P EPYC 9965 (192C) powered server with an score of 3000 (https://www.spec.org/cpu2017/results/res2024q4/cpu2017-20240923-44837.pdf) along with a comparison upgrade to a 2P Intel Xeon Platinum 8592+ (64C) based server with a score of 1130 (https://spec.org/cpu2017/results/res2024q3/cpu2017-20240701-43948.pdf). Actual SPECrate®2017_int_base score for 2P EPYC 9965 will vary based on OEM publications. Environmental impact estimates made leveraging this data, using the Country / Region specific electricity factors from the 2024 International Country Specific Electricity Factors 10 – July 2024 , and the United States Environmental Protection Agency 'Greenhouse Gas Equivalencies Calculator'.
- 9xx5-040A: XGBoost (Runs/Hour) throughput results based on AMD internal testing as of 09/05/2024. XGBoost Configurations: v2.2.1, Higgs Data Set, 32 Core Instances, FP32 2P AMD EPYC 9965 (384 Total Cores), 12 x 32 core instances, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400 (at 6000 MT/s), 1.0 Gbps NetXtreme BCM5720 Gigabit Ethernet PCIe, 3.5 TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe®, Ubuntu® 22.04.4 LTS, 6.8.0-45-generic (tuned-adm profile throughput-performance, ulimit -l 198078840, ulimit -n 1024, ulimit -s 8192), BIOS RVOT1000C (SMT=off, Determinism=Power, Turbo Boost=Enabled), NPS=1 2P AMD EPYC 9755 (256 Total Cores), 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400 (at 6000 MT/s), 1DPC, 1.0 Gbps NetXtreme BCM5720 Gigabit Ethernet PCIe, 3.5 TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe®, Ubuntu 22.04.4 LTS, 6.8.0-40-generic (tuned-adm profile throughput-performance, ulimit -l 198094956, ulimit -n 1024, ulimit -s 8192), BIOS RVOT0090F (SMT=off, Determinism=Power, Turbo Boost=Enabled), NPS=1 2P AMD EPYC 9654 (192 Total cores), 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-4800, 1DPC, 2 x 1.92 TB Samsung MZQL21T9HCJR-00A07 NVMe®, Ubuntu 22.04.4 LTS, 6.8.0-40-generic (tuned-adm profile throughput-performance, ulimit -l 198120988, ulimit -n 1024, ulimit -s 8192), BIOS TTI100BA (SMT=off, Determinism=Power), NPS=1 Versus 2P Xeon Platinum 8592+ (128 Total Cores), AMX On, 1TB 16x64GB DDR5-5600, 1DPC, 1.0 Gbps NetXtreme BCM5719 Gigabit Ethernet PCIe, 3.84 TB KIOXIA KCMYXRUG3T84 NVMe®, Ubuntu 22.04.4 LTS, 6.5.0-35 generic (tuned-adm profile throughput-performance, ulimit -l 132065548, ulimit -n 1024, ulimit -s 8192), BIOS ESE122V (SMT=off, Determinism=Power, Turbo Boost = Enabled) Results: CPU Run 1 Run 2 Run 3 Median Relative Throughput Generational 2P Turin 192C, NPS1 1565.217 1537.367 1553.957 1553.957 3 2.41 2P Turin 128C, NPS1 1103.448 1138.34 1111.969 1111.969 2.147 1.725 2P Genoa 96C, NPS1 662.577 644.776 640.95 644.776 1.245 1 2P EMR 64C 517.986 421.053 553.846 517.986 1 NA Results may vary due to factors including system configurations, software versions and BIOS settings.
- Analysis based on AMD internal data
- 9xx5TCO-001B: This scenario contains many assumptions and estimates and, while based on AMD internal research and best approximations, should be considered an example for information purposes only, and not used as a basis for decision making over actual testing. The AMD Server & Greenhouse Gas Emissions TCO (total cost of ownership) Estimator Tool - version 1.12, compares the selected AMD EPYC™ and Intel® Xeon® CPU based server solutions required to deliver a TOTAL_PERFORMANCE of 39100 units of SPECrate2017_int_base performance as of October 10, 2024. This scenario compares a legacy 2P Intel Xeon 28 core Platinum_8280 based server with a score of 391 versus 2P EPYC 9965 (192C) powered server with an score of 3000 (https://www.spec.org/cpu2017/results/res2024q4/cpu2017-20240923-44837.pdf) along with a comparison upgrade to a 2P Intel Xeon Platinum 8592+ (64C) based server with a score of 1130 (https://spec.org/cpu2017/results/res2024q3/cpu2017-20240701-43948.pdf). Actual SPECrate®2017_int_base score for 2P EPYC 9965 will vary based on OEM publications. Environmental impact estimates made leveraging this data, using the Country / Region specific electricity factors from the 2024 International Country Specific Electricity Factors 10 – July 2024 , and the United States Environmental Protection Agency 'Greenhouse Gas Equivalencies Calculator'.
- 9xx5-040A: XGBoost (Runs/Hour) throughput results based on AMD internal testing as of 09/05/2024. XGBoost Configurations: v2.2.1, Higgs Data Set, 32 Core Instances, FP32 2P AMD EPYC 9965 (384 Total Cores), 12 x 32 core instances, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400 (at 6000 MT/s), 1.0 Gbps NetXtreme BCM5720 Gigabit Ethernet PCIe, 3.5 TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe®, Ubuntu® 22.04.4 LTS, 6.8.0-45-generic (tuned-adm profile throughput-performance, ulimit -l 198078840, ulimit -n 1024, ulimit -s 8192), BIOS RVOT1000C (SMT=off, Determinism=Power, Turbo Boost=Enabled), NPS=1 2P AMD EPYC 9755 (256 Total Cores), 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400 (at 6000 MT/s), 1DPC, 1.0 Gbps NetXtreme BCM5720 Gigabit Ethernet PCIe, 3.5 TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe®, Ubuntu 22.04.4 LTS, 6.8.0-40-generic (tuned-adm profile throughput-performance, ulimit -l 198094956, ulimit -n 1024, ulimit -s 8192), BIOS RVOT0090F (SMT=off, Determinism=Power, Turbo Boost=Enabled), NPS=1 2P AMD EPYC 9654 (192 Total cores), 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-4800, 1DPC, 2 x 1.92 TB Samsung MZQL21T9HCJR-00A07 NVMe®, Ubuntu 22.04.4 LTS, 6.8.0-40-generic (tuned-adm profile throughput-performance, ulimit -l 198120988, ulimit -n 1024, ulimit -s 8192), BIOS TTI100BA (SMT=off, Determinism=Power), NPS=1 Versus 2P Xeon Platinum 8592+ (128 Total Cores), AMX On, 1TB 16x64GB DDR5-5600, 1DPC, 1.0 Gbps NetXtreme BCM5719 Gigabit Ethernet PCIe, 3.84 TB KIOXIA KCMYXRUG3T84 NVMe®, Ubuntu 22.04.4 LTS, 6.5.0-35 generic (tuned-adm profile throughput-performance, ulimit -l 132065548, ulimit -n 1024, ulimit -s 8192), BIOS ESE122V (SMT=off, Determinism=Power, Turbo Boost = Enabled) Results: CPU Run 1 Run 2 Run 3 Median Relative Throughput Generational 2P Turin 192C, NPS1 1565.217 1537.367 1553.957 1553.957 3 2.41 2P Turin 128C, NPS1 1103.448 1138.34 1111.969 1111.969 2.147 1.725 2P Genoa 96C, NPS1 662.577 644.776 640.95 644.776 1.245 1 2P EMR 64C 517.986 421.053 553.846 517.986 1 NA Results may vary due to factors including system configurations, software versions and BIOS settings.

