Our design teams use Design for Manufacturing (DFM) and Design for Test (DFT) principles to ensure manufacturability and testability of packaged devices and build in quality and reliability right from the start. We develop and integrate silicon, board and package technologies into a final product that is validated and qualified to meet customer expectations.
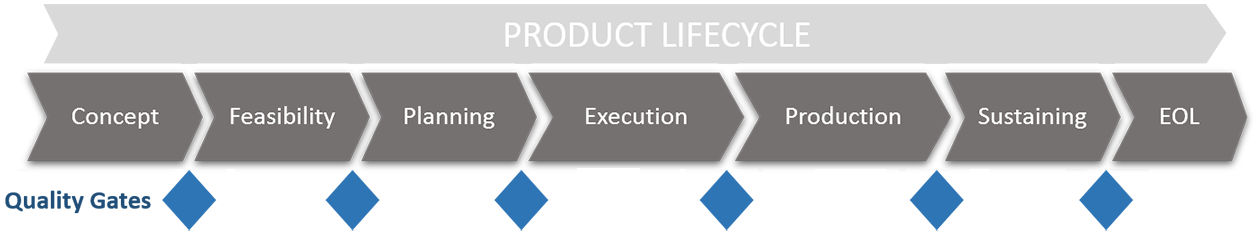
Phase Gate Process
AMD uses a rigorously governed phase gate process to embed quality from concept to production. We use these quality gates at the end of each phase to confirm that key criteria are met before the product is moved to the next stage. AMD’s product lifecycle management processes help verify that the entire lifecycle from product inception to end of life is based on industry standard guidelines.
Product Validation
AMD conducts verification testing pre-silicon and validation testing post-silicon. Pre-silicon activities include verifying the functionality of the chip and conducting various advanced chip level modeling and simulations. Post-silicon validation involves testing for speed, functionality and reliability on packaged silicon. These comprehensive tests must meet stringent requirements prior to production. Software validation is performed in parallel with hardware validation to help deliver hardware and software components that operate in harmony.
Design for Reliability (DfR)
AMD reliability methodologies are designed to overcome shrinking reliability margins for the leading process nodes. By leveraging early learning, in-depth tools expertise and machine-learning, AMD engineers shorten development processes and meet the stringent requirements of the most reliability-sensitive applications in datacentre, industrial, automotive, aerospace, and defence industries.
AMD employs techniques such as reliability design rules, budgets and guardbands which address post-stress degradation and long-term reliability.
Design for Test (DfT)
AMD design engineers place priority on the ability to detect problems quickly and identify root causes. This approach starts with Design-for-Test (DfT) methodologies and the New Product Introduction (NPI) process and extends throughout the complete product life cycle.
These techniques span digital logic, IP, memory elements, I/O boundary scanning, and many other areas. New test methodologies are measured against PPM results from customer returns.
Design for Manufacturability (DfM)
AMD Design-for-Manufacturability (DfM) engineering discipline facilitates quality, reliability, and time-to-market by focusing on mitigating risks and optimizing operational excellence. It starts with rigorous design of experiments, tests and manufacturing methodologies such as:
- DFM rules that provide performance advantages
- Characterizing devices more deeply using advanced tools & methods
- Expanded wafer qualification using three additional elements for assembly testing: electrical, thermal, and mechanical
- Enabling multiple-die performance by adding system-timing checks to characterization process