Removing Roadblocks for Scalability
Cloud computing is the new backbone of global computing. More customers than ever host their data and applications in the cloud, resulting in new agile and scalable ways of doing business.
The growing demand for cloud architecture brings the challenges of scaling operations: performance, flexibility, security, space, and cost. Intensive cloud applications such as machine learning, AI, containers, and virtualization ensure requirements continue to grow in performance and energy. To meet this growth, new levels of compute, scalability, and efficiency are required.
The new 4th Gen AMD EPYC™ 97X4 processors remove roadblocks to performance and operational scalability, opening the way forward for next-generation cloud-native computing operations.
The Next Step in Cloud Computing
4th Gen AMD EPYC 97X4 processors are optimized for cloud native workloads. With 256 threads per CPU, the AMD EPYC™ 9754 processor delivers the greatest vCPU density and best energy efficiency available on a server CPU today.1,2 With up to 128 cores, 256 threads, 128 PCIe® Gen 5 lanes (1P), and industry-leading performance per watt,2 AMD EPYC 97X4 processors represent the cutting edge in cloud computing performance.
The numbers don’t lie. Compared to competitor products, 4th Gen AMD EPYC 97X4 processors offer:
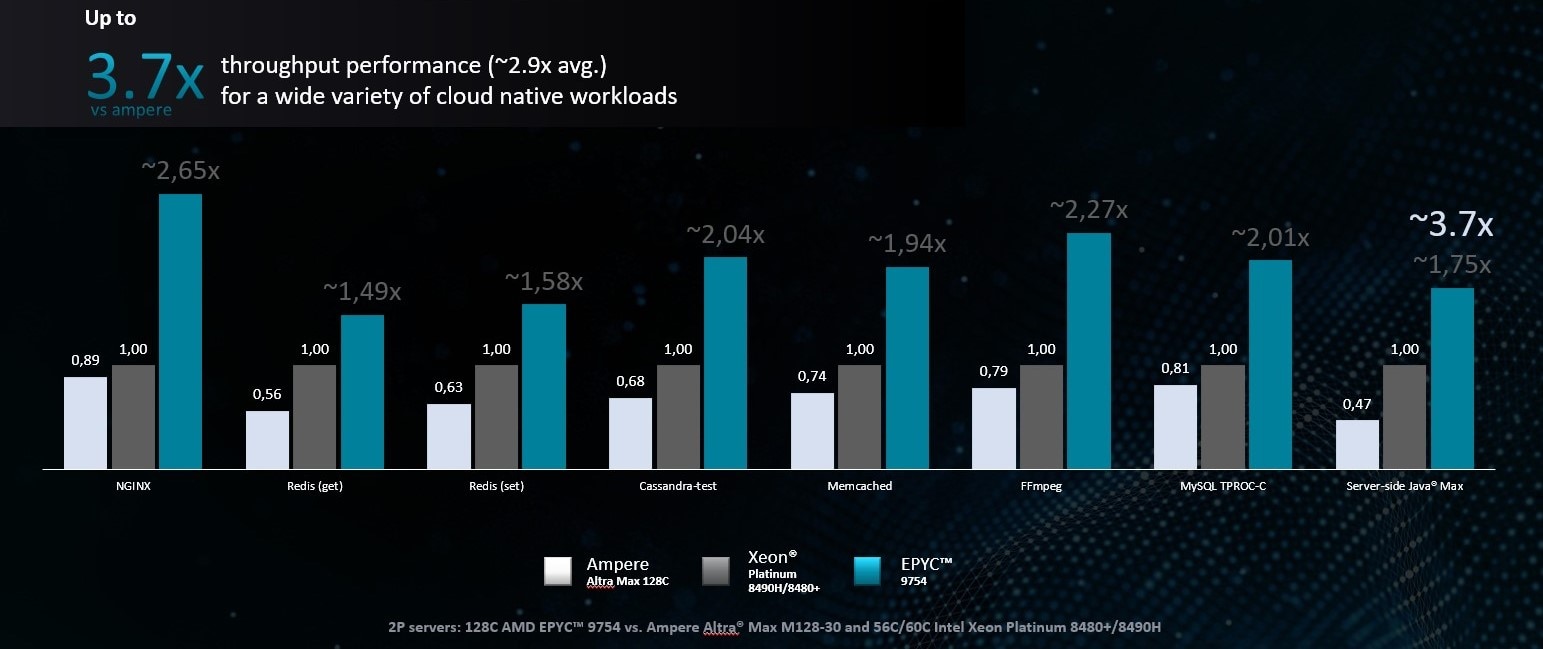
Up to 3.7x the throughput performance across a wide variety of cloud native workloads3
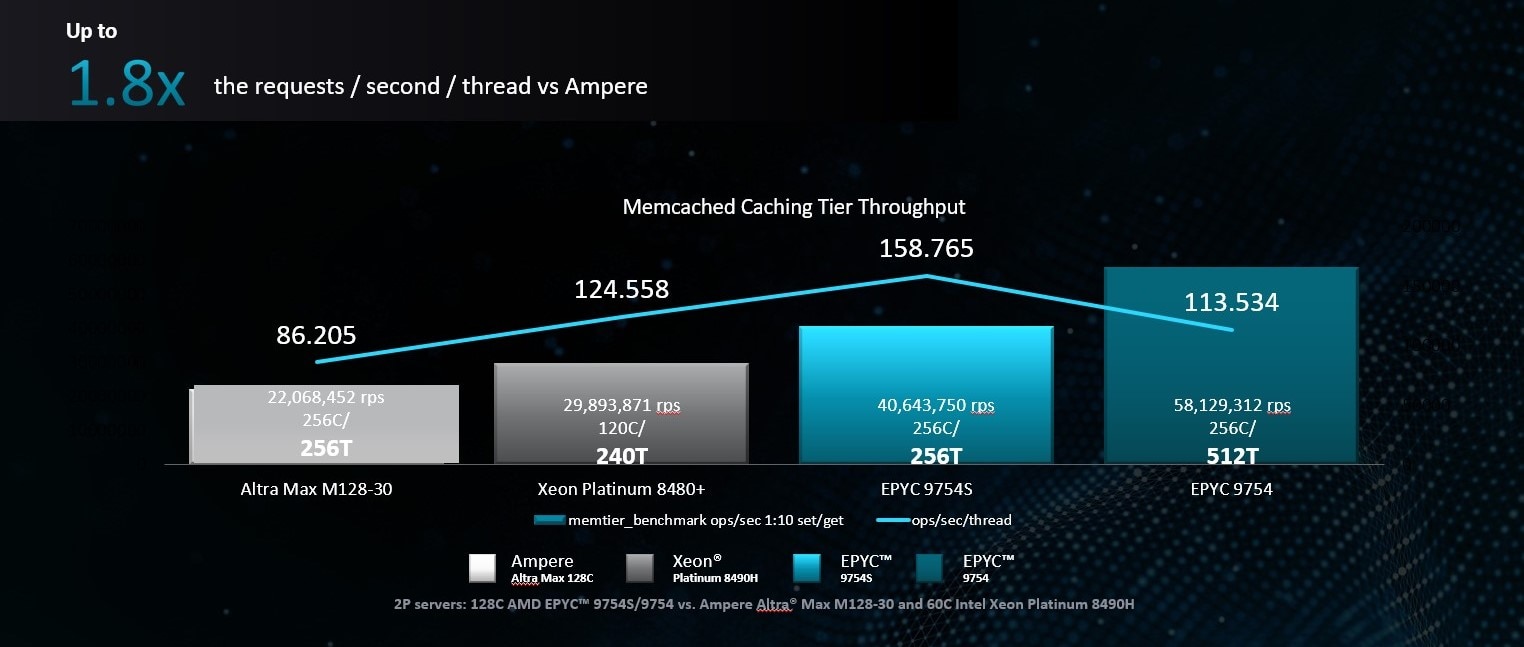
Up to 1.8x the requests per second per thread4
Up to 3x the containers per server5

Along with huge improvements to performance, those adopting 4th Gen AMD EPYC97X4 processors in their server configurations will discover a revolution in their infrastructure.
New Levels of Efficiency
While enterprise customers are looking to improve performance to handle the rising demands of increasingly intensive applications, power efficiency is paramount to ensuring operations scale affordably.
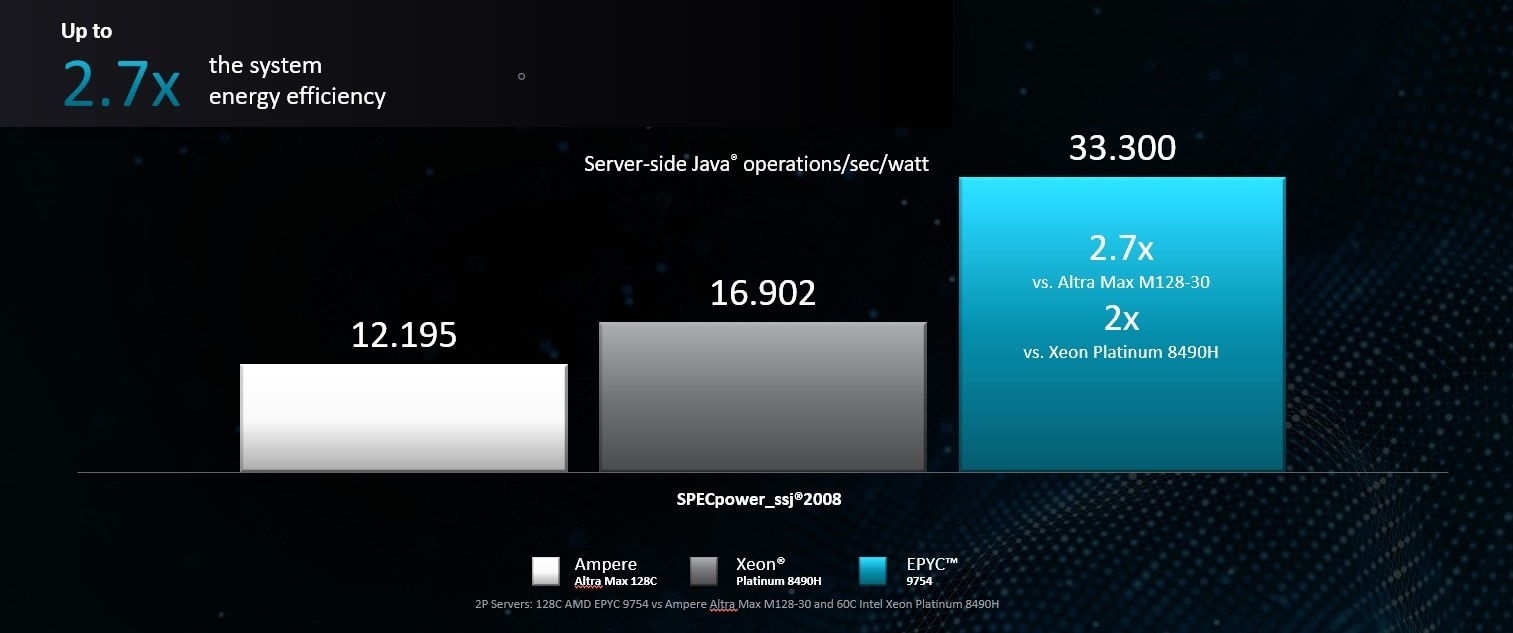
4th Gen AMD EPYC 97X4 processors deliver high performance without driving up energy usage. In fact, they lead the way in energy efficiency, delivering up to 2.7x the system energy efficiency of competitor products in 2P server configurations.6
Setting a NGINX target of infrastructure delivering 375 million requests per second, AMD estimates huge savings when compared to competitor equivalent solutions. Customers would require 65 1P Ampere® Altra Max M128-30, 128C server configurations to meet such a demand. Comparatively, only 29 4th Gen EPYC 97X4 processor configurations would be needed.7
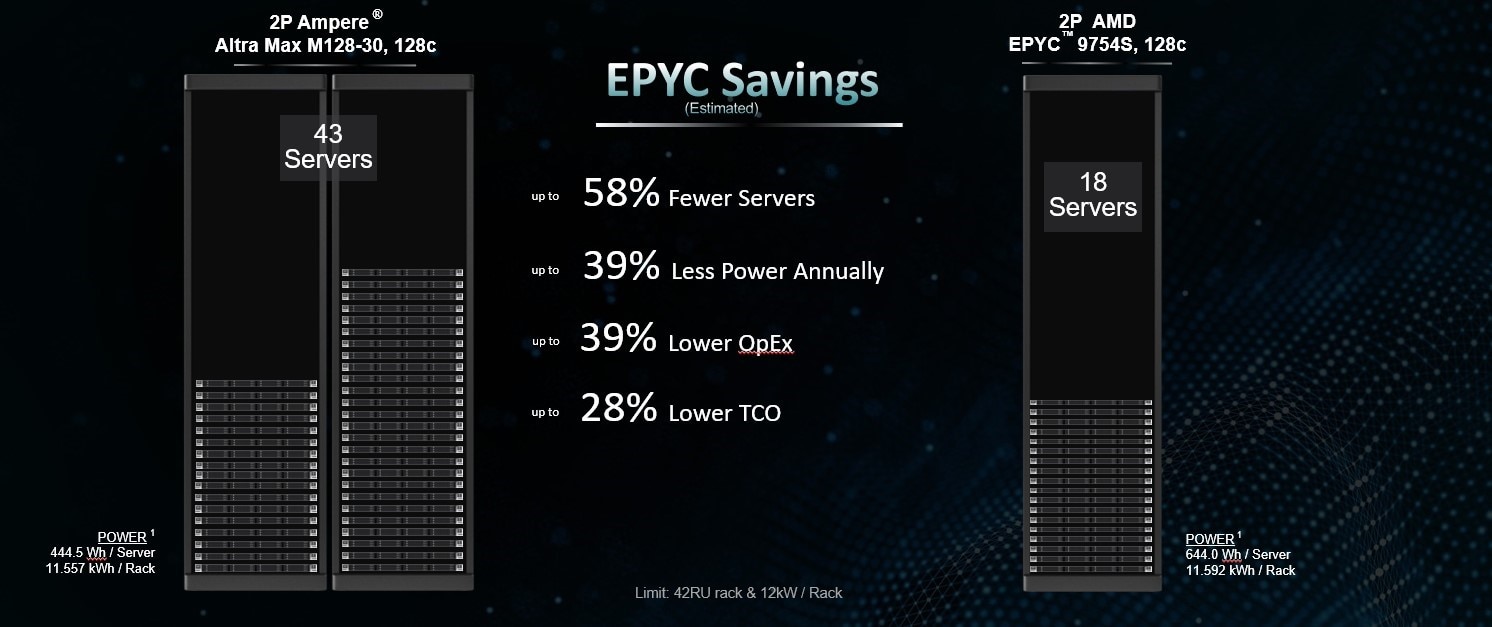
The estimated result?
Up to 55% fewer servers7
Up to 39% less power annually7
Up to 19% lower TCO7
Beyond the efficiency of the servers, there are the optimizations that come with upgrading to 4th Gen AMD EPYC 97X4 processors. X86 compatibility enables customers moving to the latest AMD EPYC™ processors to enjoy an easy upgrade path from previous generation or x86 competitor solutions, particularly from dated configurations in need of efficiency improvements.
Security Capabilities: At the Heart of AMD Servers
Performance and efficiency are what customers want, but not at the cost of security. With AMD EPYC processors, customers adopt state-of-the-art security features in the form of AMD Infinity Guard.8
As the world of data grows more complex, AMD offers a modern, multi-faceted approach to optimizing its security. Built in at the silicon level, AMD Infinity Guard features offer the advanced capabilities required to help defend against internal and external threats and keep your data safe.
Learn more about AMD Infinity Guard and how it can help protect your data.
Model |
Cores |
Threads |
Default TDP (W) |
cTRDP Range (W) |
Fbase/ Fboost9 |
SMT Configurable |
L3 Cache (MB) |
DDR5 Channels |
PCIe® Gen 5 |
9754 |
128 |
256 |
360 |
320-400 |
2.25/3.1 |
Y |
256 |
12 |
x128 |
9754S |
128 |
128 |
360 |
320-400 |
2.25/3.1 |
N |
256 |
12 |
x128 |
9734 |
112 |
224 |
340 |
320-400 |
2.20/3.0 |
Y |
256 |
12 |
x128 |
What does all this mean for AMD enterprise customers? A modern solution for the growing demand in cloud computing. It’s a solution that offers a lot while asking for little; depending on the application and workload, customers opting for 4th Gen EPYC 97X4 processors may require fewer servers, lower power usage, and lower TCO to do the same work. Across both public and private clouds, customers will enjoy a cutting-edge server configuration that delivers performance, efficiency, and robust security features from the moment it’s installed.
Reach out to your local AMD contact today to learn how 4th Gen EPYC 97X4 processors can revolutionize your cloud computing operations.
AMD Arena
Enhance your AMD product knowledge with training on AMD Ryzen™ PRO, AMD EPYC™, AMD Instinct™, and more.
Subscribe
Get monthly updates on AMD’s latest products, training resources, and Meet the Experts webinars.

Related Articles
Related Training Courses
Related Webinars
Footnotes
- EPYC-049: AMD EPYC 9754 is a 128-core dual threaded CPU and in a 2 socket server with 1 thread per vCPU delivers 512 vCPUs per EPYC powered server which is more than any Ampere or 4 socket Intel CPU based server as of 6/13/2023.
- https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/amd-epyc-9754-pb-spec-power.pdf
- Results may vary due to factors including system configurations, software versions and BIOS settings. As of 6/13/2023, see Cloud Native Workloads https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/amd-epyc-9754-pb-spec-power.pdf
- SP5-150: Memcached mem_tier 1:10 set/get ops/sec comparison based on median scores of AMD internal measurements as of 6/13/2023. See Memcached performance brief for more details: https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/amd-epyc-9754-pb-cloud-native-workloads.pdf. 2P EPYC 9754S added (configuration is same as 9754 in the paper) showing a throughput performance of 40,643,750 ops/sec at 256C/256T total (158,765/thread) is ~1.84x the ops/sec/thread compared to Altra Max M128-30 (22068452 ops/sec, 86205 ops/sec/thread). 2P 120C/240T Xeon 8490H (29893871 ops/sec, 124558 ops/sec/thread) and 2P 256C/512T EPYC 9754 (58129312 ops/sec, 113534 ops/sec/thread) shown for reference. Results may vary due to factors including system configurations, software versions and BIOS settings.
- SP5-149: Container density throughput based on sustaining ~25k e-commerce Java Ops/sec/container until exceeding SLA utilizing >90% of the total cores on composite server-side Java workload as measured by AMD as of 6/13/2023. Common container settings: allocated 40GB memory, similar disks & NICs. 2P server configurations: 2P EPYC 9754 128C/256T SMT ON, Memory: 1.5TB = 24 x 64 GB DDR5 4800, OS Ubuntu 22.04, NPS Setting: L3 as NUMA running 16 vCPUs vs. 2P Xeon Platinum 8490H 60C/120T HT ON, Memory: 2TB = 32 x 64 GB DDR5 4800, OS Ubuntu 22.04, NPS Setting: NPS 2 running 16 vCPUs vs. 2P Ampere Altra Max 128-30, Memory: 1TB =16 x 64GB DDR3200, OS Ubuntu 22.04, NPS Setting: NPS 1 running 25C. Results may vary due to factors including system configurations, software versions and BIOS settings.
- Results may vary due to factors including system configurations, software versions and BIOS settings. As of 6/13/2023, see https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/amd-epyc-9754-pb-spec-power.pdf
- All performance scores are estimates based on AMD internal testing in May & June 2023 to deliver 325 million requests. AMD performance is on an AMD reference platform with a score of 12.999M requests / sec. Ampere perf done on an Ampere Mt. Snow server with a score of 5.807M requests / sec. Analysis based on the AMD EPYC™ Bare Metal Server & Greenhouse Gas Emission TCO Estimation Tool - version 9.33 Pro. AMD processor pricing based on 1KU price as of April 2023. Ampere CPU data Phoronix.com. All pricing is in USD.
TCO analysis with a time frame of 3-year with power @ $0.128/kWh with 12kW / rack; and Power and Server Cost only are included in this TCO. This is a power only OpEx and a PUE of 1.70. NOT included in this analysis are admin cost, real estate cost, software cost as well as power for any networking and storage external to the server.
Environmental impact estimates made leveraging this data, using the Country / Region specific electricity factors from the '2020 Grid Electricity Emissions Factors v1.4 – September 2020', and the United States Environmental Protection Agency 'Greenhouse Gas Equivalencies Calculator'.
This scenario contains many assumptions and estimates and, while based on AMD internal research and best approximations, should be considered an example for information purposes only, and not used as a basis for decision making over actual testing. For more details see https://www.amd.com/en/claims/epyc4#SP5TCO-052K
- AMD Infinity Guard features vary by EPYC™ Processor generations. Infinity Guard security features must be enabled by server OEMs and/or Cloud Service Providers to operate. Check with your OEM or provider to confirm support of these features. Learn more about Infinity Guard at https://www.amd.com/en/technologies/infinity-guard. GD-183
- EPYC-018: Max boost for AMD EPYC processors is the maximum frequency achievable by any single core on the processor under normal operating conditions for server systems.
- EPYC-049: AMD EPYC 9754 is a 128-core dual threaded CPU and in a 2 socket server with 1 thread per vCPU delivers 512 vCPUs per EPYC powered server which is more than any Ampere or 4 socket Intel CPU based server as of 6/13/2023.
- https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/amd-epyc-9754-pb-spec-power.pdf
- Results may vary due to factors including system configurations, software versions and BIOS settings. As of 6/13/2023, see Cloud Native Workloads https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/amd-epyc-9754-pb-spec-power.pdf
- SP5-150: Memcached mem_tier 1:10 set/get ops/sec comparison based on median scores of AMD internal measurements as of 6/13/2023. See Memcached performance brief for more details: https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/amd-epyc-9754-pb-cloud-native-workloads.pdf. 2P EPYC 9754S added (configuration is same as 9754 in the paper) showing a throughput performance of 40,643,750 ops/sec at 256C/256T total (158,765/thread) is ~1.84x the ops/sec/thread compared to Altra Max M128-30 (22068452 ops/sec, 86205 ops/sec/thread). 2P 120C/240T Xeon 8490H (29893871 ops/sec, 124558 ops/sec/thread) and 2P 256C/512T EPYC 9754 (58129312 ops/sec, 113534 ops/sec/thread) shown for reference. Results may vary due to factors including system configurations, software versions and BIOS settings.
- SP5-149: Container density throughput based on sustaining ~25k e-commerce Java Ops/sec/container until exceeding SLA utilizing >90% of the total cores on composite server-side Java workload as measured by AMD as of 6/13/2023. Common container settings: allocated 40GB memory, similar disks & NICs. 2P server configurations: 2P EPYC 9754 128C/256T SMT ON, Memory: 1.5TB = 24 x 64 GB DDR5 4800, OS Ubuntu 22.04, NPS Setting: L3 as NUMA running 16 vCPUs vs. 2P Xeon Platinum 8490H 60C/120T HT ON, Memory: 2TB = 32 x 64 GB DDR5 4800, OS Ubuntu 22.04, NPS Setting: NPS 2 running 16 vCPUs vs. 2P Ampere Altra Max 128-30, Memory: 1TB =16 x 64GB DDR3200, OS Ubuntu 22.04, NPS Setting: NPS 1 running 25C. Results may vary due to factors including system configurations, software versions and BIOS settings.
- Results may vary due to factors including system configurations, software versions and BIOS settings. As of 6/13/2023, see https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/amd-epyc-9754-pb-spec-power.pdf
- All performance scores are estimates based on AMD internal testing in May & June 2023 to deliver 325 million requests. AMD performance is on an AMD reference platform with a score of 12.999M requests / sec. Ampere perf done on an Ampere Mt. Snow server with a score of 5.807M requests / sec. Analysis based on the AMD EPYC™ Bare Metal Server & Greenhouse Gas Emission TCO Estimation Tool - version 9.33 Pro. AMD processor pricing based on 1KU price as of April 2023. Ampere CPU data Phoronix.com. All pricing is in USD.
TCO analysis with a time frame of 3-year with power @ $0.128/kWh with 12kW / rack; and Power and Server Cost only are included in this TCO. This is a power only OpEx and a PUE of 1.70. NOT included in this analysis are admin cost, real estate cost, software cost as well as power for any networking and storage external to the server.
Environmental impact estimates made leveraging this data, using the Country / Region specific electricity factors from the '2020 Grid Electricity Emissions Factors v1.4 – September 2020', and the United States Environmental Protection Agency 'Greenhouse Gas Equivalencies Calculator'.
This scenario contains many assumptions and estimates and, while based on AMD internal research and best approximations, should be considered an example for information purposes only, and not used as a basis for decision making over actual testing. For more details see https://www.amd.com/en/claims/epyc4#SP5TCO-052K - AMD Infinity Guard features vary by EPYC™ Processor generations. Infinity Guard security features must be enabled by server OEMs and/or Cloud Service Providers to operate. Check with your OEM or provider to confirm support of these features. Learn more about Infinity Guard at https://www.amd.com/en/technologies/infinity-guard. GD-183
- EPYC-018: Max boost for AMD EPYC processors is the maximum frequency achievable by any single core on the processor under normal operating conditions for server systems.







