Article Number: PIB
Step 1 – Determine if Your Product Is Really Defective
Take a moment to review the suggestions below to be certain the processor is indeed defective. Often, the cause of the problem is not the processor itself.
- Visit the motherboard manufacturer's website and check that the processor is fully supported by the motherboard. New processors may require a motherboard BIOS update to correctly recognize a new processor.
For a list of supported processors per BIOS version, please refer to the CPU Support List document available on your motherboard manufacturer's website:
ASRock
ASUS
Biostar
Gigabyte
MSI
On your motherboard manufacturer’s website, make the appropriate selections to view the BIOS version required to support your CPU. BIOS download and installation instructions are also found on their website.
For more information, watch this video on how to update motherboard BIOS.
- Check that the memory installed is supported by your motherboard. Most motherboard manufacturers publish a list of tested and approved memory.
- Make sure that all power connectors are properly connected and that your power supply is sufficient for your system. For more information, please refer to KB article: How to Troubleshoot System Stability Issues Caused by the Power Supply Unit
- If possible, try testing the processor in another compatible system to verify that the processor is indeed faulty.
For information on how to correctly install or replace your Ryzen processor, please watch this video:
Note! It is important to always use proper care when handling the processor. Please refer to our Processor Handling Guidance page for tips and best practices.
- For information on how to correctly install or replace your Ryzen Threadripper processor, please watch this video:
Step 2: Determine What Is Not Covered by Warranty
- Try to determine if your processor defect is covered by warranty (see examples below). AMD is not liable under warranty if, through testing and examination, it is AMD’s reasonable opinion that the alleged defect or malfunction of the CPU has been caused by misuse, neglect, improper installation or testing.
- Remove the processor from the other components before you return it. Warranty service requires that only the processor be returned. Do not return the heat-sink and fan that was packaged with your processor. Upon receipt of the processor, AMD will inspect for mechanical damage and test it.
The following are common examples of the type of damage or mistreatment that will invalidate any AMD warranty:
Scratches on substrates or lids: Any scratches on substrates, 2D code, or lids affecting marking legibility.


Any bent or damaged pin(s):
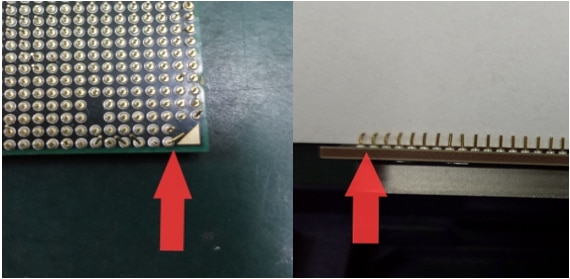
Missing pin(s):

Missing pad(s) (LGA):

Contaminated pins or I/O pads:

Gross damage:


Step 3 – Provide Required Product Information
You should include the following product information in your warranty service request:
- Processor’s Model Number (also known as the OPN).
- Processor’s Serial Number
The Processor’s Model Number and Serial Number can be found on the box and on the processor’s surface.
